Reducing the Impact
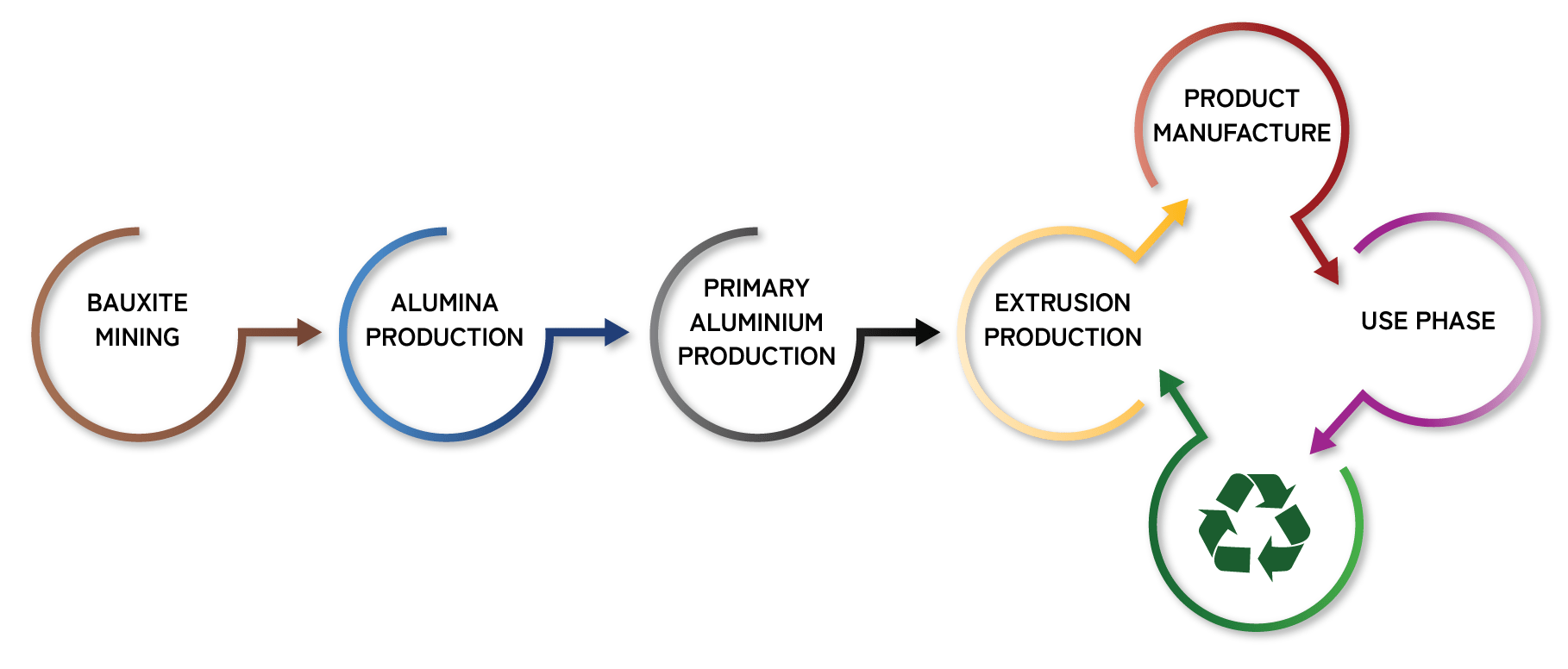
The aluminum extrusion industry is playing an important role in lessening negative impacts of growth and industrial development on our environment.
Recycling is a critical element of Extrusion’s sustainability story, but not the only part. Some important facts:
- Low-carbon primary aluminum is increasingly available as a raw material component for extrusion
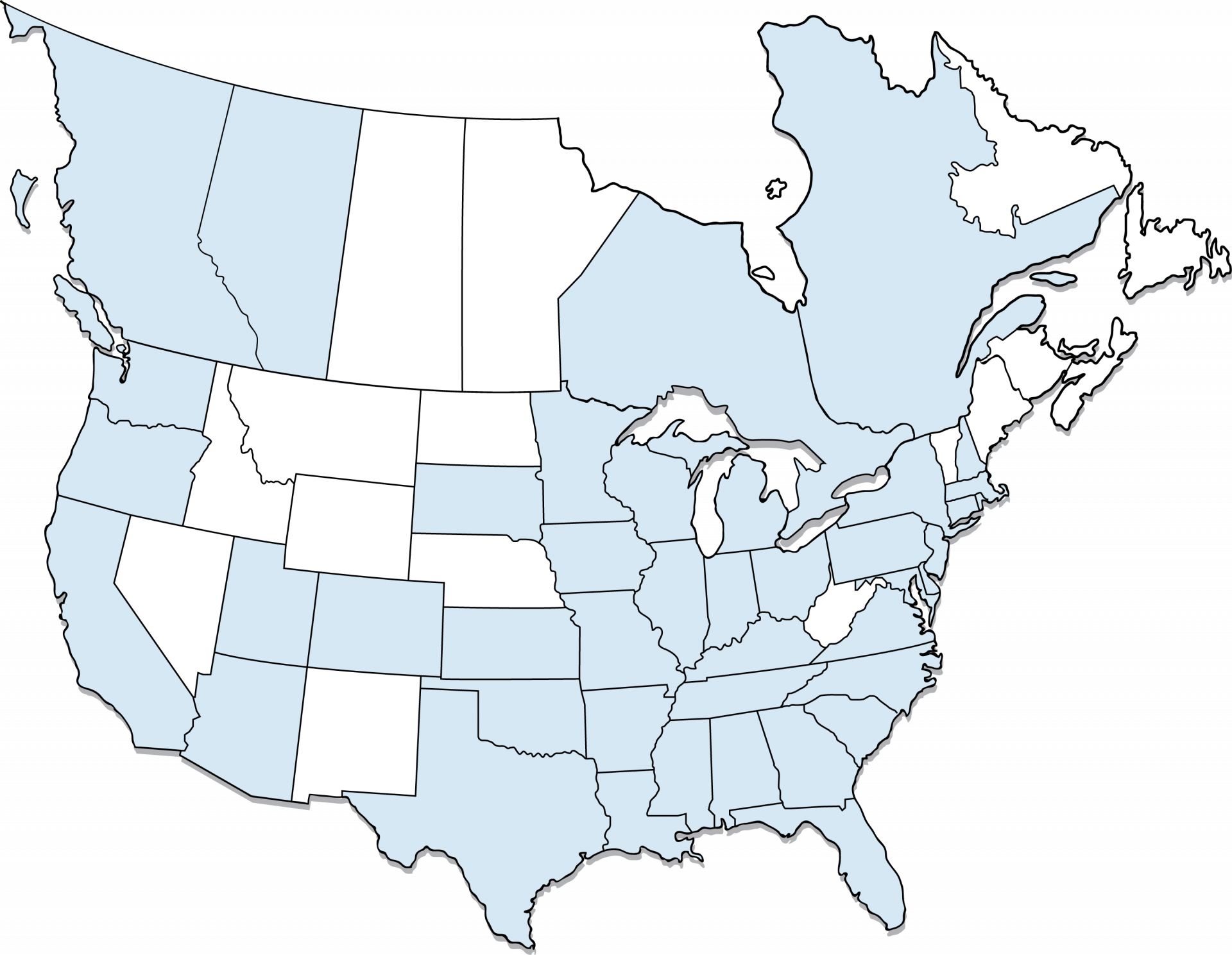
- With 170 locations in 40 U.S. states and Canadian provinces, there is an extruder nearby. Many operate their own "remelt" facilities, producing aluminum billet from scrap. That convenience and vertical integration minimizes carbon from transport.
- Extrusions help make vehicles and buildings more energy efficient
- There is a robust recycling network in North America. Studies show over 90% of aluminum from buildings and vehicles is recycled at end-of-life.
Carbon Minimization
In 1995, 16.5 tons of CO2 equivalents were generated from producing 1 ton of primary aluminum. By 2018, that had dropped to 12.0 T CO2 Eq/T of primary. Today, multiple aluminum producers are making primary aluminum available with <4 T CO2 Eq/T, in large part due to their use of hydropower or other renewable energy sources. Alcoa, Rio Tinto, and others are commercializing new smelting technologies, which promise “Zero Carbon” production.
In today’s market, aluminum is:
- Increasingly being produced from scrap, which consumes over 92% less energy than primary production
- Consumed by North American extruders at a rate of 4 billion pounds of scrap in 2021, 55% of their material need. With 170 locations in 40 states and provinces, most likely, there is an extruder nearby. Many operate their own “remelt” facilities, producing aluminum billet from scrap. That convenience and vertical integration minimizes carbon from transport.
Building Sustainability
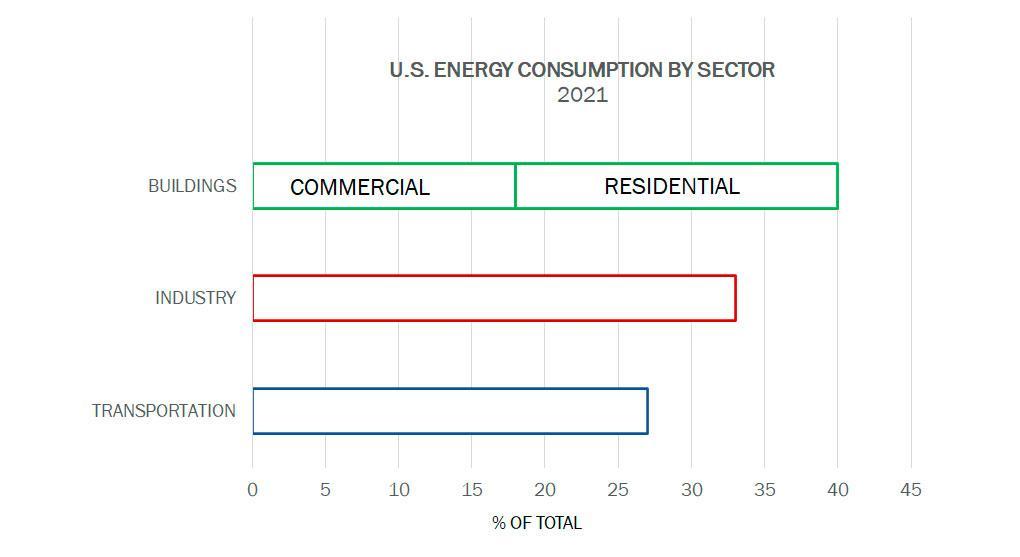
Extrusions make vehicles and buildings more energy efficient. In 2019, pre-pandemic, the U.S. consumed over 75,000 trillion BTUs of energy. In 2019, pre-pandemic, the U.S. consumed over 75,000 trillion BTUs of energy. Building operations and transportation account for two-thirds of that total.
In buildings, extruded aluminum sunshades, louvers and light shelves help reduce energy requirements for lighting and air conditioning, while extruded racking systems support building mounted photovoltaic panels generating solar power in lieu of energy from fossil fuels.
In conventional, internal combustion-powered vehicles each pound of aluminum replaces about two pounds of steel, saving 3.1 gallons of crude oil, and 20 pounds of CO2 over the life of the vehicle. Extrusion usage in the average North American car or light truck has nearly doubled, to about 50 pounds, over the past 10 years generating annual savings of over 100 million gallons of crude, and nearly 700 million pounds of CO2 per year! For battery powered vehicles, lightweighting through the use of aluminum extrusions extends vehicle range.
Recyclability for Sustainability
As an elemental material, aluminum's fundamental properties do not change with mechanical processing. Thus, it can be recycled time and again with no degradation of properties.
This infinite recyclability, combined with lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance and formability, make aluminum extrusions an important element in many sustainable solutions.
Sustainability Contributions
To learn more about extrusions’ contribution to sustainability, review:
- Aluminum Extrusion EPDs – recently released (November 2022) Life Cycle Analysis and Environmental Product Declarations covering aluminum extrusion produced in the U.S. and Canada
- In-use Benefits – an overview of the contributions that extrusion is making to more efficient autos and buildings
- Industry Sustainability Performance – learn how the Aluminum Extrusion Industry has a strong commitment to reduce the environmental impact of its own processes.
- The Role of AEC and its Members – how the Council and its members contribute to sustainability across aluminum's life cycle
Did you know?
- As an elemental metal, Aluminum is unique in that it can be recycled over and over without any degradation in physical properties.
- Over 1 billion tons of primary aluminum have been produced since 1888: 75% of it is still in productive use!
- In total, recycling represents roughly 35% of global aluminum production
- Recycling aluminum requires only about 8% of the energy required for primary aluminum production.
- Each ton of aluminum recycled, rather than produced from ore, saves:
- 24 barrels of crude oil equivalents
- Over 15 tons of fresh or seawater
- More than 9 tons of CO2 equivalents
- Substituting aluminum for other materials has substantial in-use benefits, saving energy and reducing CO2 emissions.
- The emissions savings from increased aluminum usage in transportation is so great that the aluminum industry should become "greenhouse gas neutral" in the next decade, i.e., the global warming impact from aluminum production will be more than offset by the carbon dioxide reductions from its use in transportation.